Where is it safer to keep your DevOps data backups — in the cloud or on-premise? For sure, when it comes to SMBs or large businesses, everything depends on their corporate, legal, or compliance requirements. Their security teams have a proper evaluation of the security issues of each of the deployment models for a backup and analyze which one suits them the most.
However, while many companies opt for one of the variants, others are starting to rely more on a hybrid deployment model.
Cloud Backup Strategy vs. On-Premise Backup Strategy
Building a reliable data backup strategy can be a trying task. Moreover, it requires much knowledge and skills from your DevOps or DevSecOps teams. Well, your backup and recovery strategy definitely includes analyzing and identifying the most critical parts of your DevOps data, backup methods (whether it’s a full, incremental, or differential backup), the frequency of your backups, retention, automation, monitoring, compliance, and so on and so forth.
However, the backup destination in this link is not by any means the least. Understanding different backup destinations permits administrators to adopt better backup policies and procedures that ensure the safety of the company’s critical assets, especially when it comes to the long-term storage of data.
Should I Still Keep My Backups Locally?
The on-premise backup strategy assumes you don’t send your backup elsewhere but keep them locally on your own computer, server, or any other network-attached storage (NAS).
By means, keeping your local backup has a lot of benefits, among which are:
- Better control over your on-premise backup infrastructure,
- Cost predictability, as you have a clear understanding of your upfront hardware and infrastructure costs. Thus, keeping data in-house attracts SMBs with its cost-effectiveness, as a potential data breach might result in substantially greater costs.
- Higher security as your local backup never leaves your organization. Due to the fact that some companies have security concerns about keeping their data in the cloud — there are a number of myths about the risks of storing data there — companies opt for only on-premise storage consumption. Hopefully, those are only myths as digital backup solutions are operating within the highest international security standards, like ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type 1, and SOC 2 Type 2.
- Compliance and data sovereignty, as your data always remains within your physical jurisdiction.
- No dependency on the internet, as you keep your backed-up data locally in your data center, you don’t need to rely on the internet connection that may be limited or unreliable in some cases,
All in all, a local backup strategy can guarantee data protection, availability, and accessibility in a reliable and cost-effective way securing from data breaches and hardware failures.
However, the flip side is that your local backup infrastructure may not be able to accommodate the growing data volumes, so your organization may face storage limitations.
Other downsides include the possibility of hardware failure, which leads to data loss (if you keep only local backups), and rather high costs, as you need to pay for maintenance, administration, or energy consumption.
Is the Cloud Backup Strategy Going to Win the Race?
Thanks to its flexibility, user-friendliness, affordability, remote data access, and limitless storage capacity, the cloud backup strategy is on the rise. This kind of backup strategy supposes that you keep your backups in some remote data centers hosted by cloud service providers or even backup vendors themselves.
Though cloud storage providers implement robust security measures for data protection, including encryption, compliance certifications, and access controls, you still need to take care of your backed-up data and ensure compliance with your industry regulations and internal policies.
Moreover, cloud backups rely on internet connectivity, so if you experience downtime and there is no stable internet connection, it may be hard to restore your data and continue your work without interruption.
What Is a Hybrid Backup Strategy?
Every security leader is determined to establish a solid and reliable backup strategy, though it’s one of the most critical tasks on his plate. With the fact that backing up to the cloud has become more secure and affordable, considering the combination of both local backups and cloud backups is making more sense for security leaders.
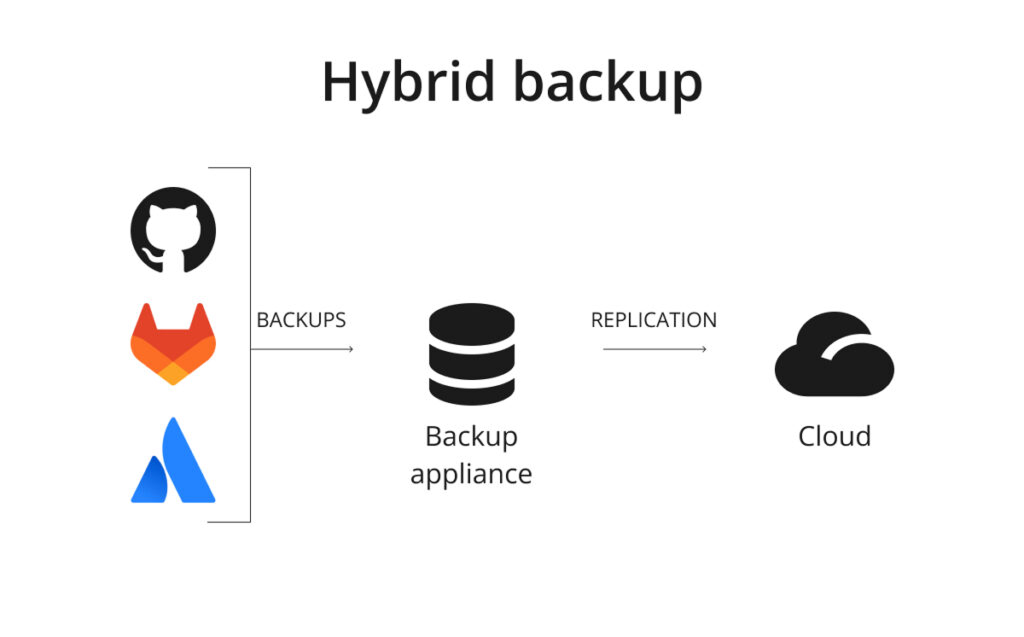
This hybrid backup approach, when you send your backups to your local device as well as your public or private cloud, permits your organization to have at least two equally working backup copies or replication plans between different storage instances.
So, if something goes wrong with one backup destination, you can always run your backup and recover your critical data from another one.
Depending on what storage dominates, the hybrid backup approach can be divided into two strategies:
- Hybrid cloud backup strategy, when the cloud storage is the main one;
- Hybrid server backup strategy, when the first backup storage is set to your local device.
No matter which storage you assign as the first one, the opportunity to back up your DevOps data to multiple storage instances and enable replication between opens the horizons for your organization to implement the 3-2-1 backup approach when you have at least three operational copies in two different storage locations, and one of those is an off-site storage instance.
Moreover, you can also implement other modern backup strategies, such as the 4-3-2 or the 3-2-1-1 backup approaches. Thus, all in your hands!
Benefits of the Hybrid Backup Strategy: An Overview
The hybrid backup approach serves as a superb balance between the on-premise backup strategy and the cloud one. It absorbed the best from both options and improved their strong sides.
Improvements from the Data Redundancy Side
Switching to the hybrid backup approach permits you to control the redundancy of your data. Due to you keeping your backups both locally and in the cloud, you can stay sure that your backed-up critical data is protected from hardware failures and any other incidents that can happen locally with your physical storage instance.
Boosting of Scalability
Sending your backups to your local storage instance and to the cloud simultaneously allows for flexible storage scaling. In the case of a server, local data center, or NAS device, you always need to buy additional equipment to fit your storage needs.
In turn, it leads to higher expenses on purchasing new appliances, but also its maintenance and administration. Having cloud storage as an option, it’s easier to leverage and accommodate your storage needs as the volumes of your DevOps data grow.
Enhanced Security and DevOps Data Restore
Keeping your backups in a few different assigned storage locations permits you to restore your critical DevOps data should the need arise quickly. For example, if your on-premise storage fails, you can restore your data from the cloud, and vice versa. Thus, your business continuity won’t be under threat.
Meeting Compliance Requirements
Often companies that seek to meet strict compliance regulations should guarantee that their mission-critical data can be easily retrieved if one of the storage destinations fails. Thus, if your organization implements the hybrid backup strategy, it can help you stay compliant with security standards.
Let’s sum up the benefits of this strategy by analyzing the following table:
| On-premise backup strategy | Cloud backup strategy | Hybrid backup strategy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security | High, as you keep your backups in your physical infrastructure. | Good, as it depends on the security measures of cloud storage providers. | Excellent, as the integration of both highly improves security. |
| Scalability | Limited, as it depends on the server/NAS device you have. | High, as you can always enlarge your storage space within your cloud storage. | Excellent, as the hybrid approach allows for flexible storage scaling. |
| Reliability & Accessibility | Good, yet depends on your precautionary measures: maintenance, and administration. | Good, yet depends on the internet connection. | Improved, as if one of the options fails, you can always use another storage to restore your backups. |
| Data redundancy | Low, as the backups are kept within your physical infrastructure, and your NAS device can suffer from hardware failures and localized incidents. | Good, as the leading cloud providers usually replicate data across multiple data centers and regions. | Excellent, you fully control redundancy by multiplying backup copies stored both locally and in the cloud. |
Conclusion
When you build your data backup and restore strategy, you need to pay close attention to various factors to meet your needs and requirements. The possibility of assigning multiple storage instances here is crucial, as it permits you to follow the 3-2-1 backup rule and guarantees a reliable data protection approach and the business continuity of your organization.









